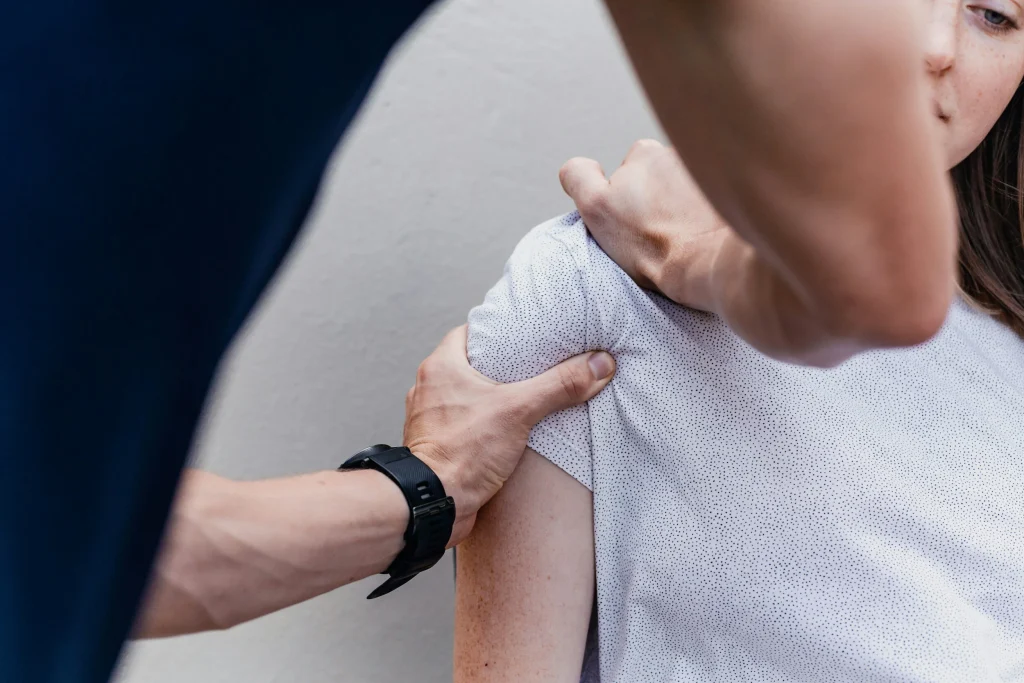
Physiotherapy plays an essential role in helping individuals regain mobility, manage pain, and improve physical function. Whether someone is recovering from an injury, managing a chronic condition, or looking to improve movement efficiency, physiotherapy offers structured and evidence-based support for long-term physical well-being.
Modern lifestyles involving prolonged sitting, repetitive movements, and limited physical activity have increased the need for professional intervention to prevent and address musculoskeletal issues.
What Physiotherapy Focuses On
Physiotherapy is centred around restoring movement and reducing discomfort caused by injury, strain, or structural imbalance. Treatment goes beyond symptom relief by addressing the root cause of pain through targeted exercises, manual therapy, and movement correction.
Rather than relying solely on medication, physiotherapy supports natural healing by improving strength, flexibility, and posture. This holistic approach helps individuals return to daily activities safely and confidently.
Common Conditions Addressed Through Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is often used to manage a wide range of physical concerns. These include back and neck pain, joint stiffness, sports injuries, post-surgical recovery, and work-related strain. It is also beneficial for posture correction, mobility issues, and injury prevention.
Athletes and physically active individuals frequently use physiotherapy to enhance performance and reduce injury risk. Likewise, individuals with sedentary routines may seek therapy to counteract muscle weakness and joint stiffness caused by inactivity. In addition to guided treatment plans, some people also explore supportive recovery options, such as using amazon magnesium oil to help relax tight muscles and ease post-activity discomfort.
Importance of Individual Assessment
A key aspect of effective physiotherapy is personalised assessment. No two bodies respond the same way to injury or stress. A proper evaluation considers posture, movement patterns, strength levels, and lifestyle habits.
Based on this assessment, a structured plan is developed to guide recovery. This ensures the approach targets specific needs and supports steady progress rather than temporary relief.
Role of Exercise and Movement Therapy
Exercise is a central component of physiotherapy. Corrective movements help retrain muscles, improve coordination, and strengthen areas prone to injury. With proper guidance, exercises are tailored to an individual’s ability and adjusted as progress is made.
Movement therapy also improves body awareness, helping individuals understand how daily habits affect posture and joint health. Over time, this awareness reduces the likelihood of recurring issues.
Recovery Beyond the Treatment Room
Physiotherapy extends beyond in-clinic sessions. Home exercises, posture awareness, and lifestyle adjustments play a significant role in long-term improvement. Consistency between sessions supports faster recovery and better outcomes.
Education is often part of the process, empowering individuals to manage their condition independently and make informed decisions about physical health.
Preventive Benefits of Physiotherapy
Beyond recovery, physiotherapy contributes to long-term prevention. Maintaining proper movement habits, flexibility, and strength reduces the risk of future injuries. Preventive care is particularly valuable for individuals with physically demanding jobs or active lifestyles.
Early intervention can prevent minor discomfort from developing into chronic conditions, improving overall quality of life.
Choosing Professional Physiotherapy Support
Selecting professional physiotherapy support involves considering experience, assessment quality, and treatment approach. A structured plan, clear communication, and focus on long-term improvement are key indicators of effective care.
People researching professional physiotherapy services may come across Benchmark Physio while exploring providers that focus on structured rehabilitation and movement-based recovery support.
Long-Term Impact on Quality of Life
Physiotherapy supports more than pain relief. Improved mobility, better posture, and increased strength contribute to greater independence and confidence. Individuals often notice improvements not just physically, but also in energy levels and daily comfort.
By addressing physical issues comprehensively, physiotherapy helps people stay active and engaged in their routines.
Conclusion
Physiotherapy is a valuable approach to managing pain, restoring mobility, and supporting long-term physical health. Through personalised assessment, targeted movement therapy, and consistent aftercare, individuals can achieve sustainable improvement and prevent future complications.
Whether used for recovery or prevention, physiotherapy offers a structured and natural pathway toward better movement and overall well-being.